- monitor free space inodes
- repair simple problems
df ( disk free )
1) By default it will show in kilobytes
2) -h stands for human-readable format
3) shows inodes, used and free
Inodes
–every file on your computer takes an INODE – a bookmark
–it's how a file is found
–maximum files 459637 files can be created on /dev/sdb1
–they are created when a partition is created
–an inode takes up space
–there is one per file
–can be a problem with a fileserver
–makefs is good at estimateing at req inodes
du ( disk usage of individual folders )
1) Default size is in blocks
2) -h is human readable form
3) --summarize will not go recursive
This command is sorta like FolderSize for Windows
fsck ( check filesystem )
1) unmount /dev/sdb1
2) fsck /dev/sdb1
3) fsck -t ext3 /dev/sdb1
4) e2fsck /dev/sdb1
Commands 2,3,4 are doing the same things.
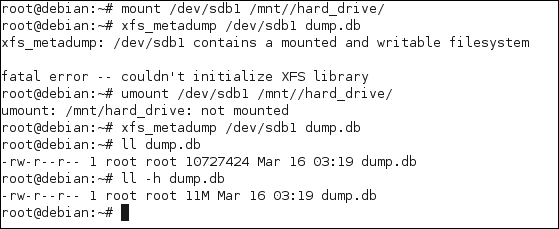
xfs_check & xfs_repair
reiserfscheck
1) mkfs -t reiserfs /dev/sdb1
2) reiserfsck /dev/sdb1
e2fsck, fsck.ext2, fsck -ext2
Repair simple problems
- most of the tools are available only for ext filesystems
debugfs
recovering a file
1) create a test file
2) use debugfs -w /dev/sdb1
3) delete the file
4) issue lsdel to list deleted files
5) undelete
dumpe2fs
dump ext2/ext3/ext4 filesystem information.
dumpe2fs on a ext2 filesystem has not “has_journal” flag set
add the journal to ext2
adding the journal uses the -O in the tune2fs program
to remove the feature use the carret symbol “^”













No comments:
Post a Comment